Mobile Agents : Introduction
- Mobile Agents are the pieces of codes that are used to store data and are independent in nature i.e. they are self-driven and does not require corresponding node for communication as they are capable of functioning even if user gets disconnected from the network.
- They are also called as transportable agents.
- They can be broadly classified into two types:
- Agents with pre-defined path.
- Agents with undefined path i.e. Roamer.
Life Cycle : Mobile Agents
The life-cycle of these agents ensures that they are :
- Able to adapt the environment i.e. either home or foreign environment.
- Able to switch among the positions of one node to other.
- Focused towards the final output.
- Autonomous.
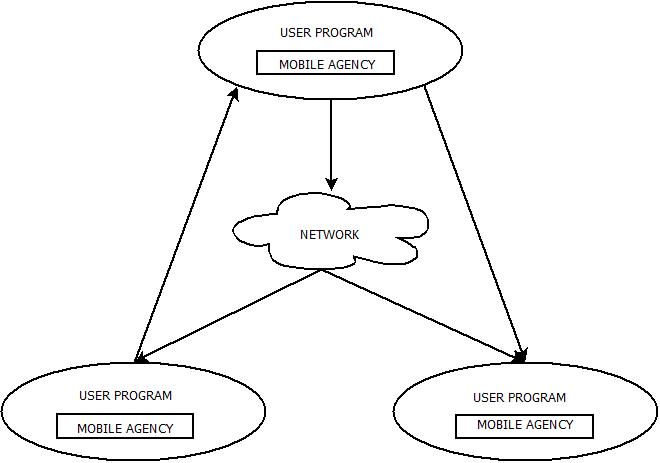
Mobile Agents : Life Cycle
Advantages : Mobile Agents
- Autonomous-Self Driven in nature.
- They possess Less delays in network.
- They are Maintainable/Maintenance Friendly.
- They are Fault tolerant.
- They possess less load on the network.
Disadvantages : Mobile Agents
- Less secured : Security is the major loop while this concept.
Applications : Mobile Agents
- Mobile Computing.
- Parallel Computing.
- Distributed Computing.
- e-Commerce.