Wireless Application Protocol(WAP) : Introduction
- Wireless Application Protocol is a programming model which is made on the concept of World Wide Web(WWW) programming model and the hierarchical design is somehow similar to TCP/IP protocol stack design.
- WAP is a standard which enables the mobile devices to interact, exchange and transmit information over the internet. It is a De-Facto standard.
- As, WAP is based upon the concept of World Wide Web, the backend functioning also remains similar i.e. HTML is used on WWW and Wireless Mark-up Language(WML) is used in WAP for using the WAP services.
- Since the WAP model is developed, it is accepted as a wireless protocol globally that is capable of working on multiple wireless technology such as mobile, printers, pagers etc.
- Another reason for opting and making WAP as De-Facto standard was its ability of creating web applications for mobile devices.
Wireless Application Protocol Model : Working
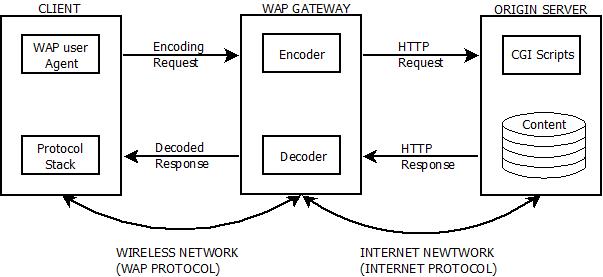
- WAP model comprises of 3-Levels that are : Client, Gateway and Origin Server.
- The WAP user agent sends a request via mobile to WAP gateway by using encoded WAP protocol i.e. called as encoding request.
- The encoding request is translated through WAP gateway and is further forwarded in the form of HTTP request to the server side where scripts are available.
- Response from the scripts and content is picked up as requested, through HTTP and is forwarded to the WAP gateway once again.
- The required HTTP response is then forwarded in decode format to the client protocol stack as the final response for the initial request made by client.
Wireless Application Protocol
Advantages : Wireless Application Protocol
- Fast paced technology.
- Open source-Free.
- Can be implemented on multiple platform.
- Independent of network standard.
- Higher controlling options.
Disadvantages : Wireless Application Protocol
- Fast Paced Technology.
- Less Secured.
- User interface(UI) is small.
- Less availability.
Applications : Wireless Application Protocol
- E-mails access.
- Weather forecasting.
- Flight information.
- Movie & cinema information.
- Traffic updates.