Mobile IP Technology : Introduction
- The mobile computing technology is highly dependent upon the concept of Mobile IP.
- Mobile IP concept was developed way back by the Internet Engineering Task Force(IETF) as a De-Facto standard communication protocol.
- Whenever any mobile device or user roads from home network to any other foreign network without possessing any change in its permanent IP address, it is called as Mobile IP concept and is achieved used mobile nodes.
- A mobile node is an attached device to the mobile user/device which keeps the track of information and position of mobile device/user. This information consists of the Home network, IP, Foreign network, Foreign IP and position includes the current or original location of the mobile user/device.
Mobile IP Technology : Architecture
The architecture consists of components. These are:
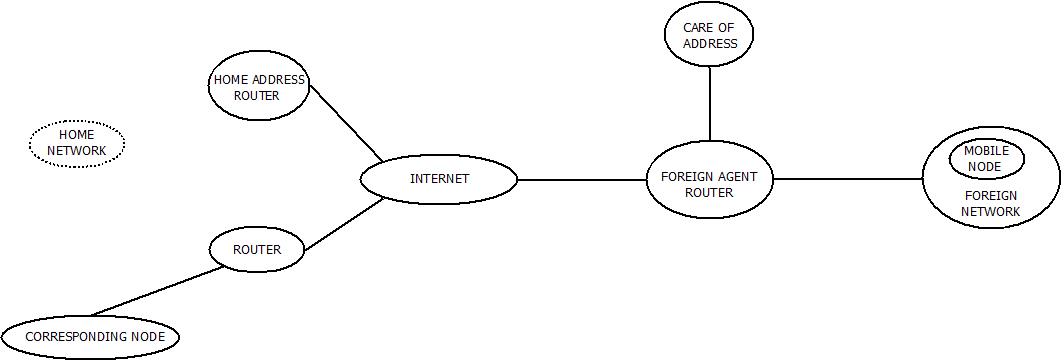 Mobile IP Technology : Architecture
Mobile IP Technology : Architecture- Foreign Agent (FA) : The agent which provides several services such as tunneling of data-grams, whenever mobile node visits foreign network.
- Foreign Network (FN) : Any network other than the network on which mobile node has a registered IP i.e. home network. Any network except home network for mobile node.
- Mobile Node (MN) : Mobile node can be called as the device or user or router that are capable of frequently changing their positions in the network without changing their original IP address.
- Corresponding Node (CN) : Partner node used for communication with mobile node.
- Home Network (HN) : The network to which mobile node originally belongs to.
- Care of Address (COA) : Current position of the mobile node/user is defined using COA. It is responsible for data packet delivery through the process of tunneling.
Functions : Mobile IP Technology
- Registration of mobile node to home agent.
- Discovery of mobile agent.
- Tunneling.
- Encapsulation.