SQL CREATE Command : Introduction
- SQL CREATE command is a type of DDL Command and is among the commands which is primarily used for creating databases and tables. The CREATE command has a particular syntax which needs to be followed In order to create databases or tables with desired structure.
- Before executing any other functions, we need to create database and it is the first step towards learning SQL.
SQL CREATE Command : Syntax
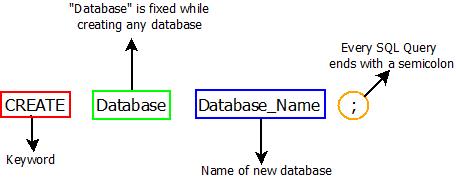
SQL CREATE Command : Syntax
SQL CREATE Command : Syntax

SQL CREATE Command : Syntax
SQL CREATE Command : Example
- Consider a database of school named as “db_school“ , containing student_details and teacher_details as two tables present in it.
Step-1 : Create the database first.
| Query : CREATE Database db_school; |
Step2 : For creating tables in this database. Firstly we need to get inside the database. This can be done using.
| Query : USE db_school; |
Step-3 : For creating tables in “db_school”, we need to use following query.
| Query-1 : CREATE Table teacher_details(Id int, Name varchar(20), Designation varchar(20)); |
| Query-2 : CREATE Table student_details(Roll_no int, Name varchar(20), Marks int); |
Here,
ID, Roll_No, Designation, Name, Marks are te columns present in the tables
And
Int & Varchar are the datatypes used in SQL.
- Both the tables are now successfully created. If the user wants to check the structure of tables and how they look like, below query can be executed.
| Query : Show Tables ; |
Points To Ponder
- To execute any query in SQL, press “Ctrl + Enter”.
- It is advisable to mention primary key while creating the tables inside the database. Example syntax is mentioned below.
| Syntax : CREATE Table employee(ID int Primary Key, Name Varchar, Dept Varchar(20) ); |
Here, “ID” of the of an employee will remain unique and can act as a primary key.
- We will be using the same database “db_school” and same tables “student_details” & “teacher_details” throughout the whole tutorial.