DBMS Architecture : Introduction
- The DBMS architecture is the foundation of any database management system, which lets the DBMS perform the functions efficiently and effectively. The whole concept of DBMS revolves around its architecture. Depending upon the architecture, database management systems are designed as centralized, decentralized, and hierarchical.
- The centralized DBMS design can be correlated with the architecture of a simple computer system such as a personal computer or laptop. The decentralized DBMS design can be correlated with client-server architecture and hierarchical DBMS can be correlated with n-Tier architecture.
- The DBMS architecture can be classified into three types as per the uses and requirements of the users.
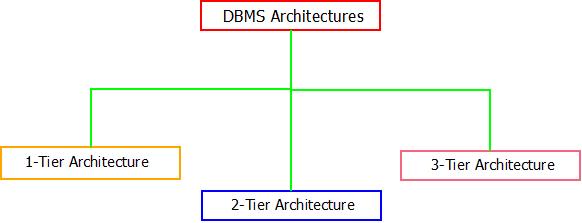
DBMS Architecture : Types
DBMS Architecture: 1-Tier
- Tier means “level/layer”. The tier-1 architecture of DBMSs is the simplest among all, which gives the user/developers the ability to let the communicate directly to the database without any intervention of 3rd It also enables the developers/users to make changes, manipulate and manage database directly. This type of architecture is mainly used by developers for their testing and data management purposes.
- Cloud-based drives and Personal computer systems can be possible examples of 1-Tier architecture.
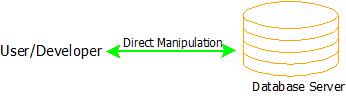
DBMS Architecture: 1-Tier
DBMS Architecture: 2-Tier
- The 2-Tier architecture of DBMS consists of two tiers. Tier-1 is the database server and Tier-2 being the users or clients of the application.
- In this type of DBMS architecture, the users of the software application deal with the database software and can find their response to the requests made by them. The user cannot manipulate the data inside the database without permission.
- Client-Server architecture can be a possible example of 2-Tier DBMS architecture.
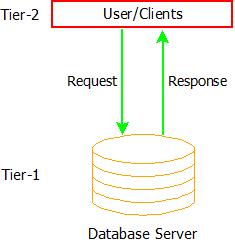
DBMS Architecture: 2-Tier
DBMS Architecture: 3-Tier
- The 3-Tier architecture of DBMS is a fully-fledged software system that is responsible for generating responses to user queries in the most efficient and suitable manner.
- The 3-Tier architecture is the most complex among all three but solves almost all the issues that occur in 2-Tier and 1-Tier architecture.
- Security, Data Backup, Recovery, Concurrency Control, and Low Data Redundancy are some of the features of a 3-Tier architecture, which makes it the most widely used database architecture.
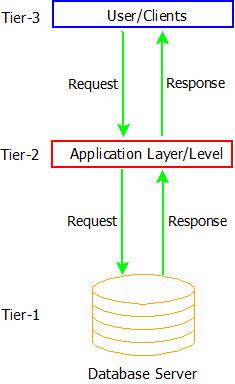
DBMS Architecture: 3-Tier
- The levels that are
used in 3-Tier DBMS architecture are:
- Database Server(Tier-1): This tier contains and deals with all the data and information. Also, it guarantees that all the data is stored in a secured manner and there might not occur a situation of data inconsistency or data redundancy.
- Application Layer(Tier-2): The application layer acts as an intermediate between the User/Client and the actual database. But it ensures to present the abstracted view of the database and provides a way to respond to the queries requested by the user by fetching the response from the database in tier-1.
- User/Client Layer(Tier-3): This is the topmost layer from where users/clients can request data and in response, the data is fetched from the database tier and passed on to the user/client tier via the application layer in the most meaningful way possible. It also provides the graphical user interface(GUI) to the users.