Relational Data Model : Introduction
- Once the E.F. Codd’s rules for DBMS was made, concept of relational data model were also introduced too by E.F. Codd. According to him, the simple databases will be called as data model only if all the data stored is in the form of tables(Columns and Rows).
- It means, each and every portion of data needs to be stored in the rows and columns of table which are linked directly or indirectly to each other. This concept of data storage in the form of tables became very popular and now it is the most widely used data model concept in the world.
- Because of simplicity, flexibility and other properties possessed by the relational data model made it the most commonly used data model for data storage and processing.
Relational Data Model : The Concept
- Relational data model represents the logical view of how data is stored in the relational databases. There exists some concepts related to this, which includes the following terms.
1. Table : In relational data model , data is stored in the tables. The tables consists of a number of rows and columns. Thus, table is used because it can represent the data in the most simplest form possible making data retrieval very easy.
2. Attribute : Any relation have definite properties that are called as attributes.
3. Tuple : Rows of table represents the tuple which contains the data records.
4. Domain : Domain is a set of values which is indivisible i.e. value for each attribute present in the table contains some specific domain in which the value needs to lie. For Example : The value of date of birth must be greater than zero. As, it cannot be negative. This is called domain of an attribute.
5. Relation : A relation in relational data model represents the respective attributes and the correlation among them.
Any relation can be denoted by : R(A1, A2, A3,…,An)
where, R Represents relation name and A1, A2, A3,…,An represents the attributes present in the relation.
- Let’s make this concept clear with an example : Consider a relation R(Roll No, Class, Marks, Age) having some attributes as mentioned. The concept can be drawn as:
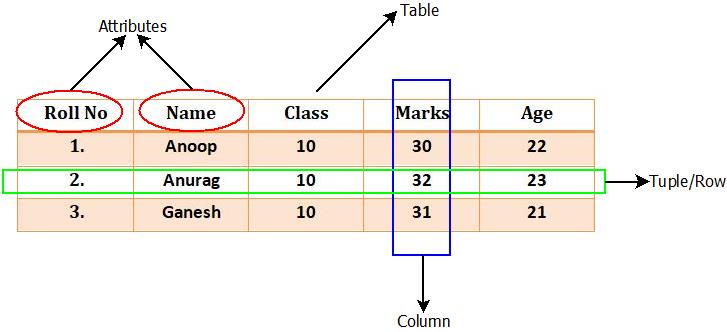
Relational Data Model : Example
Relational Data Model : Constraints
- The constraints in the relational data model are the rules and conditions that need to be followed. These rules and conditions ensures that the relation is valid and any changes or alterations made on data will not affect its operation.
- There are three major constraints based on the relational data model which are explained below.
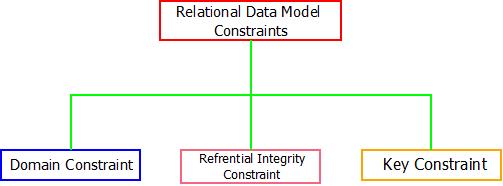
Relational Data Model : Constraints
1. Domain Constraint : This constraint is mainly applicable on the value of attributes present in the table. It ensures that the values are legitimate and comes within a pre-specified domain.
For example : Name of a person cannot contain digits (0 to 9) or special characters and Age of a person cannot be negative.
2. Key Constraint : The key constraint ensures that a table representing a relation, any row/tuple can be fetched directly using a single unique attribute called as a key. There might be a situation where, combination of multiple attribute may act as a key also.
For example : Consider a relation R(Roll No, Class, marks, Age) having some attribute. If we want to fetch the details of any student, with the help of a key it can be done.
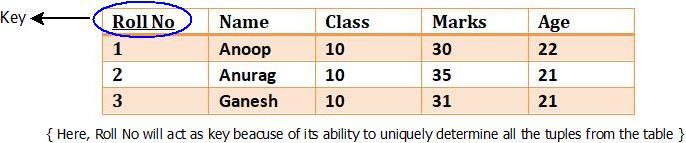
Relational Data Model : Key Constraints
3. Referential Integrity Constraint : The referential integrity works on the concept of foreign key. A foreign key is nothing but an attribute that is commonly linked between two relation using that same attribute. Both the relations/tables must contain the same attribute.
For example : Consider two relations R1(Roll No, Name, Marks) and R2(Roll No, Address, Age) of students of a school. Roll No being the common attribute will act as a key for relation R1 and can reference to Roll No attribute of relation R2 with the help of which any tuple can be retrieved from the tables.

Relational Data Model : Referential Integrity Constraints