Markov Model : Introduction
- Markov model is an un-precised model that is used in the systems that does not have any fixed patterns of occurrence i.e. randomly changing systems.
- Markov model is based upon the fact of having a random probability distribution or pattern that may be analysed statistically but cannot be predicted precisely.
- In Markovmodel, it is assumed that the future states only depends upon the current states and not the previously occurred states.
- There are four common Markov-Models out of which the most commonly used is the hidden Markov-Model.
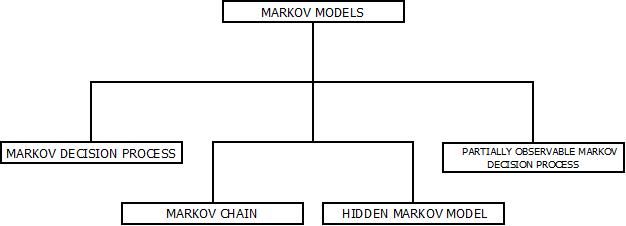
Markov Model : Types
Hidden Markov Model(HMM)
- Hidden Markov Model is an temporal probabilistic model for which a single discontinuous random variable determines all the states of the system.
- It means that, possible values of variable = Possible states in the system.
- For example: Sunlight can be the variable and sun can be the only possible state.
-
The structure of Hidden Markov-Model is restricted to the fact that basic algorithms can be implemented using matrix representations.
Concept : Hidden Markov Model
- In Hidden Markov-Model, every individual states has limited number of transitions and emissions.
- Probability is assigned for each transition between states.
- Hence, the past states are totally independent of future states.
- The fact that HMM is called hidden because of its ability of being a memory less process i.e. its future and past states are not dependent on each other.
- Since, Hidden Markov-Model is rich in mathematical structure it can be implemented for practical applications.
-
This can be achieved on two algorithms called as:
- Forward Algorithm.
- Backward Algorithm.
Applications : Hidden Markov Model
- Speech Recognition.
- Gesture Recognition.
- Language Recognition.
- Motion Sensing and Analysis.
- Protein Folding.