Data Link Layer : OSI Model
- Data Link Layer is the second layer from bottom of the OSI Model and it is responsible for successful data synchronization.
- It means Data Link Layer provides or acts as an intermediate, ensuring delivery of data message to its respective destination in the network by using the physical address of the device known as MAC (Media Access Control) Address.
- This layer translates the data received in the form of bits from physical layer into respective format and forwards it to network layer.
- Also, Data-Link Layer assembles the data message into data frames. These data frames are special structures(like letter which contains sender address and receiver address) containing the source address field, destination address fields and the data message.
- Data Link Layer is
sub divided into two fields known as:
- Logical Link Control.
- Media Access Control.

Data Link Layer : Header Format
- Logical Link Control is responsible for establishing and maintaining communication links between the devices whereas Media Access Control maintains the physical address of sender’s and receiver’s device for proper reliable delivery of data packets.
Data Link Layer : Functions & Features
- The most basic function of Data Link Layer is to synchronize data and ensure proper delivery of data message from sender to receiver device.
- Access control is feature of Data Link Layer which is responsible for deciding the control & functioning of device at particular interval of time over a network consistently of multiple device.
- Distortion, Un-delivery of data packets and noise in data packets results in error and this is prevented using Data Link Layer and this feature is called Error Control.
- Even before sending the data packets to receiver, adding sender’s & receiver’s address to the frame for reliable data delivery known as physical address(MAC Address) is done using features of physical addressing.
- Framing & Flow control are other features of the Data-Link Layer where Framing is responsible for generating data frames & Flow Control ensures that speed of data transmission by sender and data absorption by receiver are balanced. It ensures that faster data transmission and slow data absorption or slow data transmission and faster data absorption must not occur.
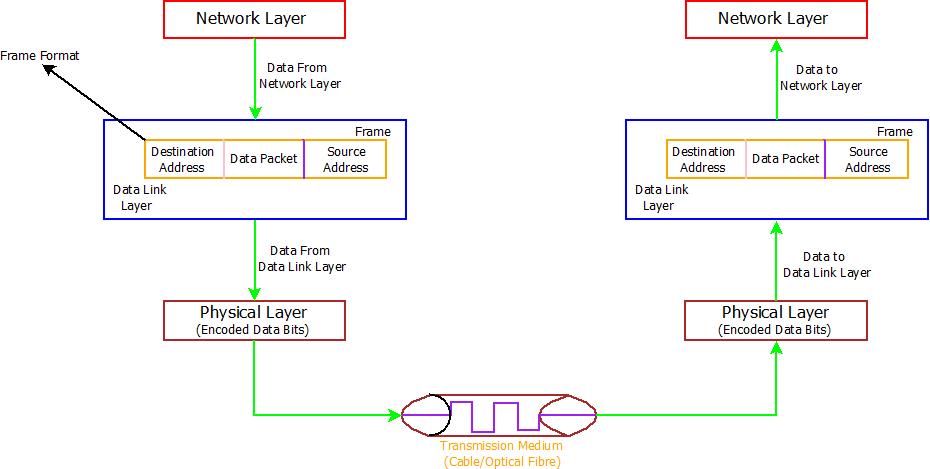
Data Link Layer : Architecture