Transport Layer : OSI Model
- The Transport Layer is the middle layer(4th Layer) of the OSI Model. The Transport-Layer acts as the transition point between the functions performed by Upper layers(Application Layer, Presentation Layer, Session Layer) & Lower layers(Network Layer, Data Link Layer, Physical Layer).
- This layer is responsible for end to end data transmission service using connection oriented or either through connection-less protocols.
- Data received from Upper layers application are combined into data streams and are transmitted to the receivers end in exact format as it was in original.
- Hiding of sensitive details of data from networks and providing data transmission in a transparent mode is also done by the transport layer itself.
Transport Layer : Functions & Features
- Segmentation : Large data is divided into smaller segments at the senders end and then these smaller segments are recombined in exact format before it is received at receivers end.
- Error Control : Distortion, Un-delivery of data packets and noise in data packets results in error and this is prevented using Transport Layer too and this feature is called Error Control.
- Flow Control : Transport-Layer ensures that faster data transmission and slow data absorption or slow data transmission and faster data absorption must not occur.
- Transport-Layer performs Multiplexing & De-multiplexing functions too.
- Connection oriented service using TCP(Transmission Control Protocol) Protocol & Connection less service using UDP(User Data-gram Protocol) Protocol are performed by transport layer.
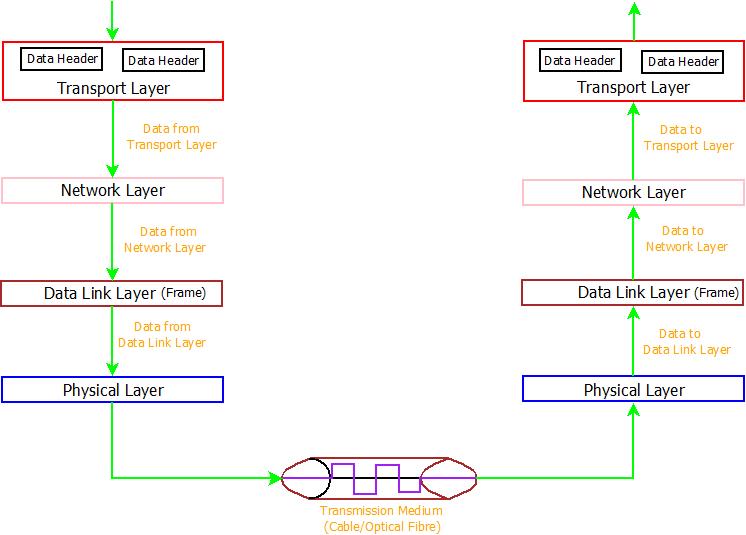
Transport Layer : Architecture
Transport Layer : Devices
- Network Devices.
- Gateways.