Cables in Computer Networks : Introduction
- Cables are the one of the most important component in any network. Cables in computer networks acts as the transmission medium through which data transmission takes place from one node to other. The cables in computer networks are classified as :
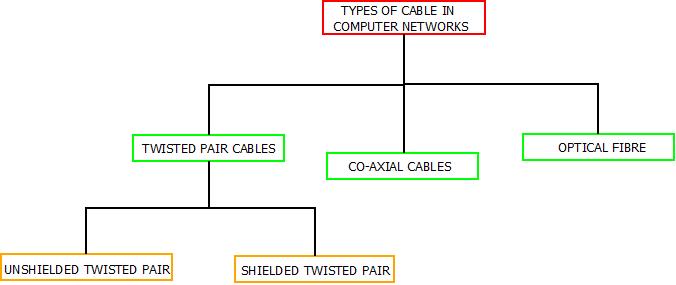
Cable Categorization : Computer Networks
Cables In Computer Networks : Twisted Pair Cables
- Two or more than two
insulated wires when twisted together forms twisted pair cables. These cable
can further be classified into two types based on their features and
usability.
- Un-Shielded twisted pair(UTP).
- Shielded Twisted Pair(STP).
A) Un-Shielded Twisted Pair(UTP)
- The most commonly general purpose cables used in the computer networks world are un-shielded twisted pair cable. They do not have any special coating or shield on the upper layers which results in high electromagnetic interference and hence named as un-shielded.
- Cables used for LANs and Telephones are unshielded twisted pair cables.
- Because of cheap nature, easy installation and maintenance, they have high demands.
- Unshielded twisted pair cables are used for voice and data transmission single handed-ly.
- Copper is used for making UTP cables.
B) Shielded Twisted Pair(STP)
- The basic difference between UTP and STP is, shielded twisted pair cables contains a special coating on the top of the wire. This coating prevents leakage of electromagnetic interference which results in high data transmission speeds.
- These cables are laid under the ground and are difficult to maintain.
- This leads to higher installation cost and maintenance cost.
- Copper is used for making STP cables.
Cables In Computer Networks : Co-Axial Cables
- Co-axial cables has lesser electromagnetic interference because of its double coating on over the core of the cable. Thus, resulting in higher bandwidth and less data losses.
- Co-axial cables are also called as radio guided cables i.e. RG-59 cables.
- These cables are much thicker than twisted pair cables having a diameter of range “0.4 to 1” inch.
- Copper is used for making Co-Axial cables.
- Long distance telephone lines is the example of co-axial cables.
Cables In Computer Networks : Optical Fiber
- Optical Fibers are commonly known as backbone cables. They have the highest bandwidth among all the types of cables available.
- Optical Fibers are made by combining glass and plastic together which results in a durable, flexible and cylindrical cables.
- Because of their glass and plastic architecture, they are quite thin and sensitive.
- Optical fibers can
be divided into three major parts:
- Core : The center most part.
- Cladding : layer on an optical fiber which ensures that no two individual cables comes in a direct contact.
- Jacket : Outermost covering over the optical fiber.
- The concept of optical fiber is based upon “Total Internal Reflection”. Thus, data travels in the form of light with the speed of light forming a zigzag pattern inside the optical fiber.
Features of Optical Fibers
- They have wider temperature range i.e. they does not break or lose shape whenever temperature changes.
- As plastic and glass are used to make optical fibers, EMF does not have any effect on it.
- No short circuits.
- Data transmission over a long distance can be done without regenerating the signals.
- Optical Fibers are highly expensive and are not used in small organisations.
Cables In Computer Networks : Comparison Among Specifications of Cables
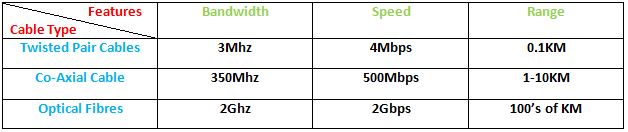
Cable Comparison : Computer Networks