Physical Layer : OSI Model
- Physical Layer is the bottom-most layer in the layered architecture of the OSI Model and it is associated with all the electrical, mechanical and functional aspects of the transmission media for information transmission(Sending or Receiving) over the internet.
- Physical layer deals with all the physical devices that can be used for data communication in a network including the types of cables and transmission modes such as Simplex Mode, Half Duplex Mode and Full Duplex Mode.
- Also, the topology of any network which forms the fundamental structure of any network is defined under the Physical-Layer.
Physical Layer : Functions & Features
- The basic function of Physical-Layer in the OSI Model is to send and receive bits in the form of “1 & 0”(Binary Value) only.
- Physical Layer is responsible only for transmitting the data bits through the network with the help of physical devices (such as cables, HUBs, Repeater etc.) connected in the network irrespective of what data the bits actually holds.
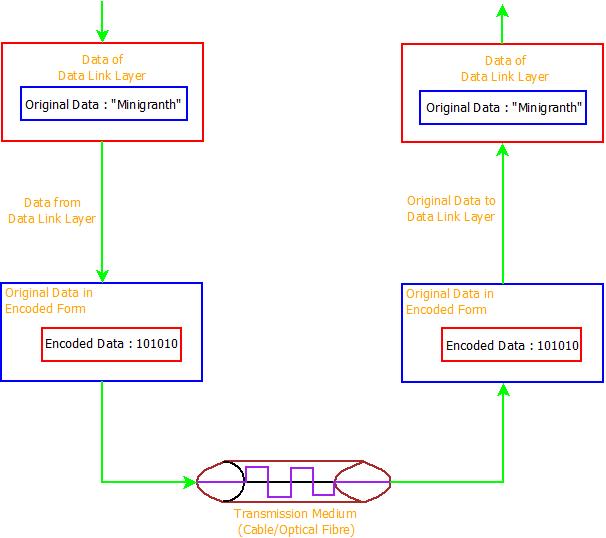
- Also, physical layer defines how the data received from above layers will be encoded into binary(0 & 1) and then how will the data bits be further decoded to its original form. The Physical Layer is responsible for it.
- Defining and dealing with the synchronization, physical topologies, bandwidth, rate of transmission and data channel are some of the other features of the Physical Layer.
- The interface for the data transmission to Data Link Layer is provided by the Physical-Layer.
- Consider some data is received by the Physical-Layer from one device and needs to be transmitted in a network. Then the data will first be converted into data bits using encoders and then will be transmitted to physical layer of other device where these bits will be further decoded and later will be sent to Data Link Layer in the original for.
Physical Layer : Architecture
Physical Layer : Devices
- Transmission Cables.
- Repeater & HUBs.
- Multiplexers.
- Transmitters.
- Receivers etc.