TCP/IP Reference Model: Introduction
- The OSI reference model was the first communication model and was termed as general-purpose model because of its ability to fit in any type of network but without fitting the protocols in. Due to its inability to fit protocols, TCP/IP reference model which is commonly known as Internet Model was developed in year 1983 by US Military Wing called ARPANET.
- In 1983 January 1, TCP/IP was made active permanently for the commercial use. From then, TCP/IP has made a revolution in the field of networking and telecommunication as it was able to overcome the drawbacks of general purpose OSI Model.
- TCP/IP stands for Transmission Control Protocol with the help of which, protocol implementation over the network can be achieved.
- The TCP/IP model also has a layered architecture which allows easy data communication along with the facility of integrating multiple protocols. The layout remains similar to OSI Model but the number of layer, their functionalities and properties got changed.
- This Internet Model(TCP/IP) comprises of only four layers as compared to seven layers of OSI Model. These four layers are generated by combining the layers of OSI model internally so that protocols can be implemented. These layers have fixed positions too and their positions cannot be altered.
- Application Layer, Transport Layer, Internet Layer and Network Access Layers are the four layers of TCP/IP Model.
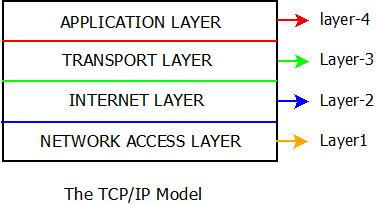
Architecture And Layers : TCP/IP Reference Model
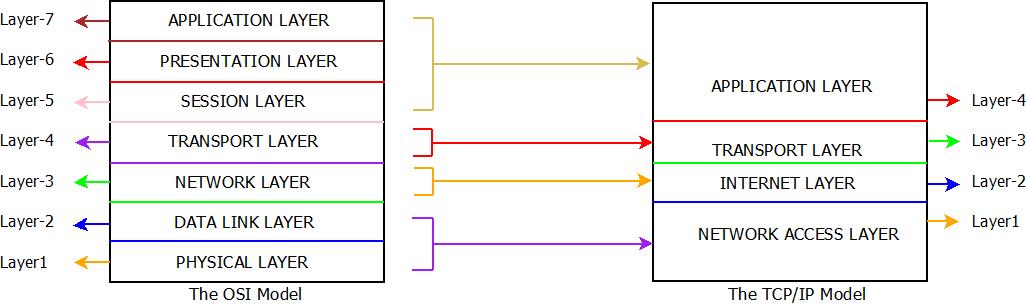
Architecture : TCP/IP Reference Model
a) The Network Access Layer
- The Network Access Layer of TCP/IP reference model is also known as the Host-to-Host or Host-to-Network layer as it is responsible for performing roles of the Physical Layer along with the functions of Data Link Layer.
- Data in the form of bits received in the Network Access Layer are connected in the form of data packets to Internet Layer.
- Network Access Layer = Data Link Layer + Physical Layer.
b) The Internet Layer
- Internet layer is also called Network Layer which is responsible for establishment of connection to send or receive data packets between multiple users or nodes or devices or networks. This layer is placed on the 2nd position from bottom.
- The Internet Layer en-routes the data packets from source to destination through the process of routing with the help of various routing techniques and routing protocols.
c) The Transport Layer
- The Transport Layer performs the same functions and have similar features as that in OSI Model. The functionality of Transport Layer is, it provides end to end data transfer by using the technique of connection oriented services between sender and receiver with the help of various protocols.
d) The Application layer
- The Application Layer resides on the top of the TCP/IP reference model as line in OSI Model. The functionality of Application Layer of TCP/IP reference model is to provide interface between users and the applications. In some cases depending upon the requirements, it can perform the functions of Session Layer(to provide sessions) and Presentation Layer(data representation).
- Application Layer = Session Layer + Presentation Layer + Application Layer .
Advantages : TCP/IP Reference Model
- Use of protocols implementation and their support.
- Each layer has its definite structure and functionality which makes OSI model simple and easy to use.
- Use of layered architecture.
Disadvantages : TCP/IP Reference Model
- As some layers has multiple functionalities, it is more complex than OSI Model where each layer has separate functions and services.
- The TCP/IP reference makes use of protocols. But, in case of replacement of any protocol, difficulty and issue might arise.